Unveiling the Future: Medical 3D Printing's Transformative Role
The advent of 3D Printing technology has ushered in a new era in the medical field, offering groundbreaking approaches to treatment, device manufacturing, and patient care.
Utilizing ELEGOO 3D Resin Printers, healthcare professionals can now produce highly customized medical devices, patient-specific models, and even complex tissue structures with precision and efficiency.
This article explores the multifaceted applications of medical 3D printing, highlighting its significant benefits and the potential it holds for revolutionizing healthcare practices.
Also! If you're interested in medical 3D applications within healthcare, we'd suggest you take a look at our 3D Printer for Dentistry post, (Dentistry and 3D Printing work nicely together).
Outline
- Transforming Patient Care with Custom Medical Devices
- The Process and Technology Behind Medical 3D Printing
- Regulatory Landscape and Ethical Considerations
- The Future of 3D Printing in Medicine and Healthcare
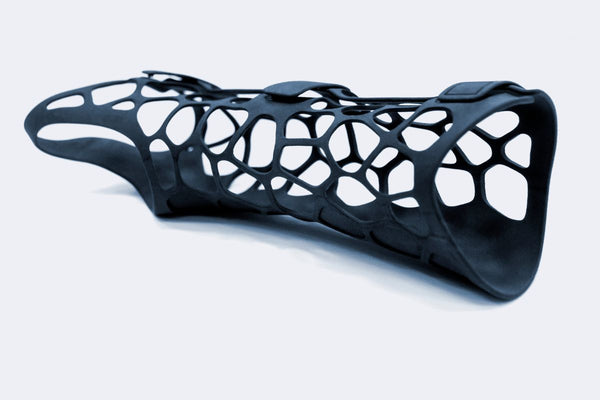
Transforming Patient Care with Custom Medical Devices
The customization capability of 3D printing technology stands as its most significant advantage in the medical field.
This allows for the creation of medical devices tailored to the unique anatomical features of individual patients, enhancing the effectiveness of treatments and interventions.
From prosthetics and implants to surgical tools and patient-specific models for preoperative planning, 3D printing is making waves across various medical specialties.
Not only does this improve patient outcomes by ensuring a perfect fit and reducing the risk of complications, but it also streamlines the healthcare process, cutting down on operation times and overall costs.

The Process and Technology Behind Medical 3D Printing
Medical 3D printing employs several technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), each suited to different applications within the medical sector. The choice of materials ranges from biocompatible plastics for surgical tools to metal alloys for durable implants and even bio-inks for potential tissue engineering.
Despite the vast potential, the process comes with its challenges, such as ensuring the sterility of printed objects and achieving the required precision for complex internal structures, highlighting the need for continuous innovation and quality control in medical 3D printing.
For medical practitioners interested in our 3D Printers, we'd encourage you to take a look at our ELEGOO Mars 4 Ultra.
Regulatory Landscape and Ethical Considerations
As medical 3D printing evolves, so does the regulatory landscape designed to safeguard patient safety.
Bodies like the FDA are actively developing guidelines to regulate the use of 3D printing in manufacturing medical devices, ensuring they meet stringent quality and safety standards. Beyond regulation, the technology raises ethical questions, especially concerning the printing of biological materials and the prospect of organ manufacturing.
These considerations necessitate a careful balance between innovation and ethical responsibility, ensuring advancements in 3D printing serve the best interests of patients and society.
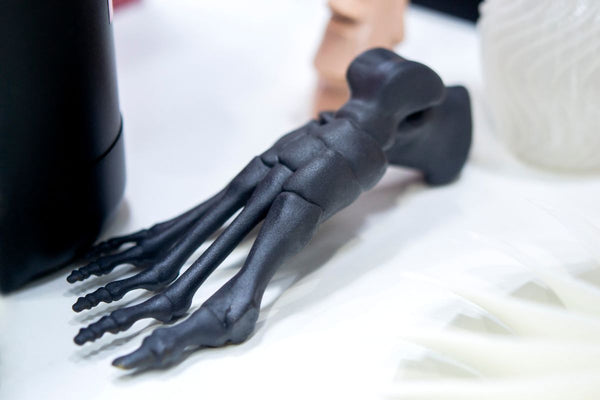

The Future of 3D Printing in Medicine and Healthcare
The future of medical 3D printing promises even greater innovations, with emerging trends pointing towards more personalized medical care and the expansion of regenerative medicine.
As research progresses, the possibility of printing fully functional organs for transplantation becomes increasingly plausible, potentially addressing the chronic shortage of donor organs.
Moreover, the integration of 3D printing with other biomedical technologies could lead to breakthroughs in personalized medicine, where treatments and devices are tailored not just to the physical dimensions of patients, but also to their genetic profiles.
Summary
- Customization of medical devices through 3D printing significantly improves patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
- Technological advancements in 3D printing are enabling the production of medical-grade devices with a range of materials, though challenges remain in ensuring quality and safety.
- Regulatory and ethical considerations are crucial in guiding the responsible development and application of medical 3D printing.
- The future of medical 3D printing holds promising advancements in personalized medicine and regenerative therapies, potentially revolutionizing the medical industry.
Medical 3D printing stands at the forefront of technological innovation in healthcare, offering solutions that were once deemed impossible.
As the technology continues to evolve, its integration into the medical field will undoubtedly lead to more effective treatments, improved patient care, and the opening of new frontiers in medical research and application.